来源:小编 更新:2024-11-30 05:43:25
用手机看

Bitcoin, the pioneering cryptocurrency, relies heavily on blockchain technology to facilitate transactions. At the heart of this technology are Bitcoin addresses, which serve as the digital equivalent of bank account numbers. In this article, we will delve into the basics of Bitcoin addresses, their structure, and their importance in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
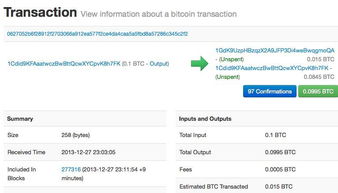
A Bitcoin address is a string of characters that uniquely identifies an individual or entity on the Bitcoin network. It is used to send and receive Bitcoin, similar to how a bank account number is used to send and receive money. Each address is generated using a combination of public and private keys, which are cryptographic tools that ensure the security and integrity of transactions.

Bitcoin addresses typically consist of 26-35 alphanumeric characters, including both letters (case-sensitive) and numbers. They are derived from a public key, which is a long string of numbers and letters. The public key is then hashed using a one-way cryptographic function, which produces a fixed-size output known as a hash. This hash is then encoded into a human-readable format, which is the Bitcoin address.

The process of converting a public key to a Bitcoin address involves several steps:
Generate a public key from a private key using elliptic curve secp256k1, which is the cryptographic algorithm used by Bitcoin.
Hash the public key using SHA-256, a cryptographic hash function.
Apply RIPEMD-160 to the SHA-256 hash to create a 160-bit number.
Convert the 160-bit number into a binary format.
Prepend a version byte to the binary number, which indicates the network and address format.
Double the binary number and check the most significant bit. If it's 0, the address is valid; if it's 1, the process is repeated.
Convert the binary number back into a hexadecimal format.
Convert the hexadecimal number into a base58-encoded string, which is the final Bitcoin address.

Bitcoin addresses are crucial for the functioning of the cryptocurrency network. Here are some key reasons why they are important:
Security: Bitcoin addresses are designed to be secure, making it difficult for unauthorized users to access the funds associated with them.
Privacy: Users can create new addresses for each transaction, which helps to protect their privacy and prevent link analysis.
Accessibility: Bitcoin addresses can be easily shared and used across different platforms and devices.
Scalability: The use of addresses allows for a decentralized and scalable system, as there is no need for a central authority to manage them.
There are several types of Bitcoin addresses, each with its own format and use case:
Legacy Addresses: These are the original format of Bitcoin addresses and are still widely used. They start with the number '1' and are 26-35 characters long.
Bech32 Addresses: Introduced in 2017, Bech32 addresses are designed to be more efficient and secure. They start with the characters 'bc1' and can be shorter than legacy addresses.
SegWit Addresses: Segregated Witness (SegWit) is a protocol update that improves the scalability of the Bitcoin network. SegWit addresses start with the characters 'bc1' and are similar to Bech32 addresses.

Bitcoin addresses are an essential component of the cryptocurrency ecosystem, providing a secure and efficient way to send and receive Bitcoin. Understanding their structure and importance can help users navigate the world of Bitcoin with confidence. As the cryptocurrency space continues to evolve, it's crucial to stay informed about the latest developments, including changes to address formats and security practices.
